Distributed Autonomous Operating System (DAOS)
While WLTH's investment platform is still evolving, its vision for a participative community requires a new type of operating system. We are building a distributed, autonomous operating system (DAOS) to enable safe, transparent, and permissionless collaboration. We believe this system is essential for any decentralized group to coordinate effectively and remain compliant.
What Is It?
DAOS is a hybrid Web2/Web3 software solution designed to coordinate and reward decentralized groups. It uses smart contracts to enforce payments and structure, allowing for modular strategies and policies agreed upon by the collective. Our goal is to automate project management, keeping teams aligned through transparent workflows and incentives with minimal overhead.
How Does It Work?
The Orchestrator directs pre-defined workflows via smart contracts, enabling collaboration between all actors in the system—be they human, AI, or code. These actors function as service providers to each other and the protocol, which in turn collects royalty fees. Actors are rewarded for their services, while token holders benefit from the platform's smooth operation.
The Distributed Autonomous Operating System (DAOS) has four core components:
Actors / people / roles involved in the task (team and community).
Escrow ‘smart vault’ allowed to drawdown funds from Treasury according to pre-specified rules to pay for the work (smart contract.
Task Nodes - software component that binds the actors, the task and the escrow smart contract together for the duration of the task.
Orchestrator - an intelligent task management system to orchestrate workflow between the actors, the work order / task that needs to be done (the Orchestrator).
The Orchestrator (rules engine) at the heart of the system which allows for provision of leadership and structure and guidance in a non-hierarchical, distributed environment and is configured and operated by community-agreed policies and governance.
The Actors
Actors are users participants in the system and come in three flavours - Specifier, Worker & Checker.
Specifier - a qualified person who specifies the work task to be done
Worker - the domain-qualified person carrying out the work
Checker- the domain-qualified person verifying the work was completed by the Worker to the standard set by the Specifier.
Actors can be from the community, third parties, or even automated algorithms. Users can qualify for jobs at any time and either self-select roles or be matched by an Orchestrator. A social graph prevents collusion, while our reputation system and on-chain monitoring provide social proof and verification of qualifications.
Tasks
The Orchestrator creates and manages all tasks, which can be performed by both community and core contributors. Tasks vary in required skill level, can be time-sensitive, and may be one-off or recurring. For accountability, all tasks are logged and must be auditable, transparent, and capable of manual verification by default.
The Orchestrator
Similar to an AI Director in a video game, the DAOS Orchestrator dynamically manages our ecosystem. It provides permissionless coordination by taking inputs from the community and core contributors, then matchmaking tasks with the right people and rewarding them appropriately.
Using these pieces, and some of the core technology already developed in WLTH, we can:
Build workflows to specify, create, manage and pay for tasks permissionless.
Compose complex workflows between multiple participants of varying skill levels and responsibilities are transparent and fully auditable.
Includes anti-collision and anti-collusion tech to manage community / core contributors relationships too.
Now imagine all rewards and all work being co-ordinated and rewarded by this system, modulated and led by community consensus.
There have been expressions of interest to CW in spinning out the DAOS technology in its own right.
Payments
Our system's core permissionless feature is its payment process, which is governed by a custom ERC-4626 escrow smart contract. This contract includes time-locks, vesting, and multi-sig address locks to manage proportional payouts. Payment splits are set by the Orchestrator during task creation and are time-locked upon completion to allow for dispute arbitration.
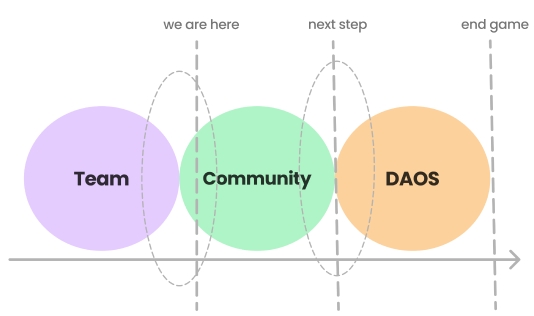
Progressive Decentralisation (“Bootloading”)
Today, WLTH is a blend of people and technology, all at various stages of independence and automation - however, decentralisation is well underway. Over the coming months, the core contributors will continue to uncouple themselves more and more from the operation of the community, platform and protocol before it can exist as a decentralised autonomous system in perpetuity.
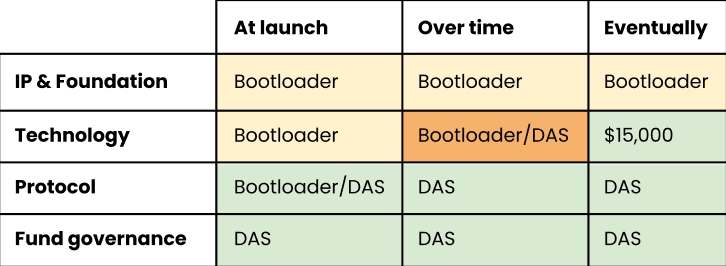
Bootloader Activities
A DAS is designed to be a self sustaining, decentralised system, however, there will be centralised entities that create and initiate components of the DAS before surrendering control of them.
These activities are known as “bootloader” activities, named after the software that starts a computer.
Last updated
